The Latest Microplate Technologies: Expanding Laboratory Function and Extending Scientific Reach
New microplate products are bringing techniques such as confocal microscopy out of imaging and screening facilities and into the realm of basic research applications
Microplate technologies have evolved over the years, and so has the scope of their applications. For instance, single-mode systems have given rise to multi-mode platforms using advanced spectroscopy detection methods.
Evolving microplate technologies have served to miniaturize and automate biochemical assays as well. Surface-plasmon resonance, biosensor detection, biologic screening, and others are all enabled by advanced microplate hardware and software analysis tools. Technologies born in the spectroscopy cuvette or under the microscope have grown into high-content cellular imaging and screening systems.
The latest microplate systems have evolved to bring advanced functions, such confocal microscopy, beyond dedicated cellular imaging and screening facilities and into the realm of basic research labs and their applications. Here is a brief perspective of microplate evolution and some developments that are leading the way.
Single-mode Microplate Readers
Microplate readers miniaturize and merge workflows by combining spectroscopic detection with automatable microplate handling.

Absorbance, fluorescence, and luminescence are the most common modes of microplate detection — covering the visible, ultraviolet, or full range light spectrum.
- Colorimetric and intrinsic absorbance measurements, such as those needed for protein and nucleic acid quantitation, are very common uses for these devices.
- Fluorescence can measure the reaction of a reagent with a substrate or with a protein, although intrinsic or fluorescent nucleic acid labels may also be detected with great sensitivity.
- Luminescence can add another layer of sensitivity and flexibility over fluorescence.
Single-mode detection systems may be best suited for well validated routine applications, such as unlabelled or labelled protein or DNA quantitation, without the need for advanced or multiplexed features (shown is the Molecular Devices SpectraMAX single-mode absorbance reader).
Multi-mode Microplate Readers
Multi-mode systems combine two or more detection modes in a central platform.

- In addition to the detection modes above, specific measurements such as time-resolved fluorescence (TRF) and fluorescence polarization (FP) can be applied.
- Additional modules can be available as upgrades to enable Western blot, imaging, and other capabilities.
- Plate shaking, incubation, washing, and other duties can enable complete end-to-end workflows for complex imaging, ELISA applications, and others.
While single-mode devices can perform dedicated function with relative fast speed and throughput, multi-mode devices can combine workflows and broaden the scope of lab operations (shown is the BioTek Cytation family of multi-mode readers).
Biochemical Assays
Biochemical assays that were once relegated to the reaction tube, vessel, or column can now be performed in microplate format, enabling a wide-range of applications designed to speed up the discovery process.
- Primary assays, such as those during the early stages of the small molecule or biologic development processes, often involve biomolecule interaction, catalysis, enzyme kinetics, or other cell-free activities.
- Advanced microplate systems can now be coupled with microplates and other reagents, and fixed with reactants, substrates, or indicators.
- Reactions can be concentrated within the plates and can be measured in real-time.
- Scale and throughput can be increased to enable true high-throughput screening of compound libraries, engineered proteins, and single cell clone isolation.
- Diverse biomolecules — such as antibodies, soluble receptors, and peptides — can be assessed rapidly for basic functionality, saving time and resources in the therapeutic development process.
Cellular Imaging Systems

Once the domain of the microscope, cellular imaging and analysis has now been integrated with the microplate world. Systems for High-content and High-throughput Screening (HCS, HTS) applications incorporate objectives, filters, imaging and light channels, environmental and incubation conditions, and more — all built into these sizable devices.
- Advanced microplate imaging technologies have created a valuable discovery resource beyond HCS and HTS applications — and new products are now emerging to harness this power (shown is the BioTek Cytation 1 cell imaging multi-mode reader).
- This breadth of features equates to a range of capabilities including imaging: live cells, stem cells, plant cells, tissues slices, whole organelles, and 3-D cell matrices.
- The ability to image such a broad range of cells and tissues translates to a vast multitude of cell-based assays, all capable by means of a central platform.
- High-content imaging produces high density data, and innovative software solutions are designed to help make sense of the valuable while ignoring the unnecessary data.
Confocal Imaging Systems
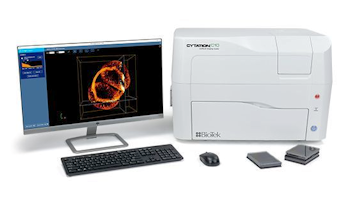
The essential elements of confocal imaging systems can now be fitted within a small-sized mutli-modal microplate reader.
- Systems like the BioTek Cytation 10 (shown right) integrate a six objective microscope turret with a laser-based spinning-disk confocular module.
- This module is paired with LED-based widefied module.
- Detection is performed by sCMOS camera.
- The confocal components are housed along with a transmitted light module, a multi-mode multichromator detection module, a plate carrier and other features seen with typical microplate readers.

- A system like this allows widefield imaging, for faster acquisition of large images at lower magnification.
- Switching to confocal mode allows high-resolution imaging of 3D structures and intracellular details.
The aray of multi-modal functions allows collection of biochemical assay data and cellular metabolic data, for instance, all using the same instrument and microplate samples (shown is the Molecular Devices ImageXpress Micro confocal HCS system).
Outlook
New system designs are modular, allowing addition of components as they are needed. Software features are powerful and allow for automated operation.
The latest microplate technologies are integrating greater power and resolution than microplate readers of yesterday — opening a new world for basic researchers from a wide field of disciplines.
View Molecular Devices Microplate listings.
View BioTek Microplate listings.
Updated August 2021










