Electron Microscope Price, including Cost of 50 Different Models
A Comprehensive Guide to Electron Microscope Models, Prices, and Cost Considerations
The price of an Electron Microscope (EM) varies dramatically. According to the type, configuration, components, resolution, and other important factors, instruments can cost $75,000 - $10,000,000. New Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM) can cost $70,000 to $1,000,000, while used instruments can cost $2,500 to $550,000 depending on condition. Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM) cost $100,000 to $10,000,000 for new and $125,000 to $900,000 for used instruments. Dual Beam or SEM/FIB instruments can cost $85,000 to $3,000,000 for new and $20,000 to $600,000 for used.
In this article, we detail the price factors and considerations involved in purchasing new or used Electron Microscopes.
 From the invention of the first Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) over 90 years ago, advancements in technology have led the way towards greater resolving power for an ever-broadening scope of applications. Today there are many different types and models of Electron Microscopes (EMs) available, with applications ranging from imaging cellular structures and organelles by TEM to mapping the surface of nanomaterials using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) techniques.
From the invention of the first Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) over 90 years ago, advancements in technology have led the way towards greater resolving power for an ever-broadening scope of applications. Today there are many different types and models of Electron Microscopes (EMs) available, with applications ranging from imaging cellular structures and organelles by TEM to mapping the surface of nanomaterials using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) techniques.
The most notable attribute of electron microscopy is significantly increased resolution over conventional light and fluorescence microscopy. SEM uses a focused beam of electrons which interact with electrons of the sample providing details on the surface topology and composition. The resolution is typically in the low nanometer (nm) range. TEM is similar to SEM in that a beam of electrons is projected onto a sample. Major differences include the ability to map subsurface details of samples, with resolution down to the single-electron, sub-nanometer level.
In the over 50 years since the electron microscope was first commercialized, a diverse market of instruments and components has come into view with a wide range of prices. Commercially available instruments can be grouped into three types, based on application:
- Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM) and Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope (STEM) are used for imaging and analysis of features from electron transparent thin samples.
- Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM) are used for imaging and analyzing the sample surfaces and topology.
- Dual Beam or SEM/Focused Ion Beam instruments are capable of surface imaging by SEM and creating cross sections to enable internal feature viewing.
Along with higher resolution and functionality comes a more expensive price tag. SEM instruments can range in price from a few thousand to a few hundred thousand dollars. TEM instruments can reach the multi-million-dollar range. Used and refurbished microscopes can be obtained at a fraction of those prices, which is a major consideration for most laboratories. Before searching for new, used, or refurbished instruments, however, it’s important to identify the right device, not just for your budget, but for your needs and intended applications. Three initial considerations may include:
- What type of specimens do you plan to image and what are the special considerations for sample preparation?
- What is the resolution required to observe the specimen and the features of interest?
- How large is the sample to be imaged?
Understanding details regarding intended applications will help in identifying instrument types and models. Instruments can then be narrowed down by factors such as budget, components and add-ons, customizable features and other details.
Electron Microscope Price List (Updated Feb. 2022)
Here is a table of many common types and models of Electron Microscopes and current price information:
|
Model |
Type |
Approximate Price (Used) |
|
Amray 1800 FE |
SEM |
$12,300 - 30,800 |
|
Bausch & Lomb LE 2100 Nanolab |
SEM |
$3,600 - 300,000 |
|
FEI FIB 830 |
SEM |
$400,000 - 550,000 |
|
FEI Quanta Series |
SEM & FIB |
$30,000 - 200,000 |
|
FEI Tecnai Series |
TEM |
$225,000 - 395,000 |
|
FEI XL30 |
SEM |
$65,000 - 150,000 |
|
FEI Titan 80-30 |
TEM |
$875,000 |
|
FEI Altura Dualbeam |
FIB/SEM |
$235,000 |
|
FEI CM 100 |
TEM |
$130,000 |
|
FEI CM 120 |
TEM |
$150,000 - 175,000 |
|
FEI CM 200 |
TEM |
$175,000 - 300,000 |
|
FEI CM 10 |
TEM |
$95,000 - 125,000 |
|
FEI CM 12 |
TEM |
$161,000 |
|
FEI SEM 515 |
SEM |
$10,000 |
|
FEI SEM 550 |
SEM |
$10,000 |
|
FEI EM 208 |
TEM |
$125,000 |
|
FEI FIB 200 |
SEM |
$75,000 |
|
Hitachi TM 1000 |
SEM |
$22,000 |
|
Hitachi TM 4000 II |
SEM |
$225,000 |
|
Hitachi S-2400 |
SEM |
$17,500 - 42,000 |
|
Hitachi S-4500 FEG |
SEM |
$31,000 - 115,000 |
|
Hitachi S-4700 FEG |
SEM |
$195,000 |
|
Hitachi S-500 SEM series |
SEM |
$2,300 - 13,850 |
|
Hitachi S-5200 SEM |
SEM |
$15,000 |
|
JEOL 733 |
SEM |
$10,000 |
|
JEOL 1200ex series |
TEM |
$150,000 - 250,000 |
|
JEOL JCM-5000 Neoscope |
SEM |
$11,800 - 27,000 |
|
JEOL JEM-1400 Plus |
TEM |
$225,000 |
|
JEOL JEM-2011 |
TEM |
$150,000 |
|
JEOL JSM-5200 |
SEM |
$13,000 |
|
JEOL JSM-5300 |
SEM |
$45,000 |
|
JEOL JSM-6300 series |
SEM |
$9,300 - 12,000 |
|
JEOL JSM-6400 series |
SEM |
$23,500 - 100,000 |
|
JEOL JSM-6700 series |
SEM |
$7,500 - 110,000 |
|
JEOL JSM-7000f |
SEM |
$75,000 |
|
JEOL JSM-7700F |
SEM |
$23,500 - 50,000 |
|
JEOL JSM-840 A |
SEM |
$33,700 |
|
JEOL JSM-T330A SEM |
SEM |
$8,000 |
|
Leica Stereo Scan 260 |
SEM |
$11,400 |
|
Micrion 9500 |
SEM |
$225,000 |
|
MMT Xfactor |
SEM |
$35,000 |
|
Tescan Vega TS 5130SB |
SEM |
$16,000 |
|
Tescan Vega II |
SEM |
$35,000 |
|
Zeiss EVO 25 |
SEM |
$95,000 |
|
Zeiss EVO 53H |
SEM |
$135,000 |
|
Zeiss LEO 1550 FE-SEM |
SEM |
$150,000 |
|
Zeiss LEO 435VP |
SEM |
$75,000 |
|
Zeiss LEO 982 |
SEM |
$125,000 |
|
Zeiss SUPRA 55VP |
SEM |
$550,000 |
|
Zeiss SUPRA-40 |
SEM |
$240,000 |
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Price Factors
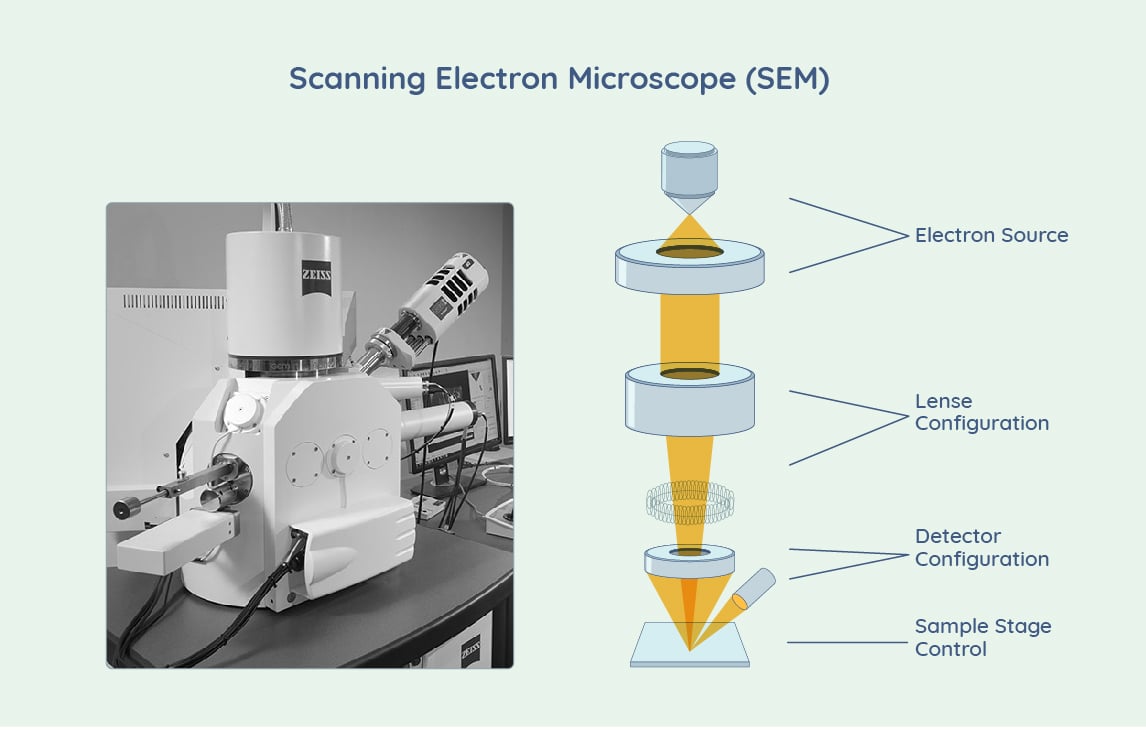
- Type – Floor model SEMs generally have elevated electron beam strength and resolving power. They also have a greater need for vibrational isolation and power consumption. Benchtop models may be best suited for general applications and locations where space is a premium.
- Resolution – Price can correlate with the power of resolution as the strength and quality of the electron beam increases. High-contrast lenses over standard lenses, and other details regarding optics, can further impact price.
- Components – The emitter, or the electron source, can come in three different types. Tungsten filament is the most common and is made out of high-grade tungsten. The other two types are a solid-state crystal and a field emission gun. Several detectors are typically used to detect scattered electrons, working together to help produce the electron microscope image. The type and quality of emitters and detectors correlate with price. SEM, and EM in general, has a requirement for vacuum operating conditions, the specifications of which may impact pricing as well.
- Configurations – Whether the instrument has single, double, or triple electron beam performance plays a factor in price. The arrangement of the emitters and detectors is important, as is the use of data processing software and user interface features.
- Stage controls – Stage controls allow the specimen to be rotated, raised, lowered, and tilted. Depending on the type of stage controls there may be 5 axes of control. The quality, degrees of movement, and added functionality all have bearing on price.
- Image display – Depending on the electron microscope there could a wide variety of image displays that could come with the system. Some common configurations are large screen, single image, dual image, and quad image displays – all with an impact on price.
- Sample requirements – Depending on the type of sample to be imaged, there may be certain requirements for sample accommodation. Weight, size, ventilation, or barriers required to fit the specimen all can factor into the cost of the setup.
- Customization – Costs can increase if the application requires additional functionality such as static backscatter diffraction (EBSD), for deeper sample analysis, or add-on devices such as a Wavelength-Dispersive X-Ray spectrometer (WDS), tensile and heating stages, radiation shielding or hot cells, or other components. Upgradability is another factor to consider which may have an influence on price.
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Price Factors
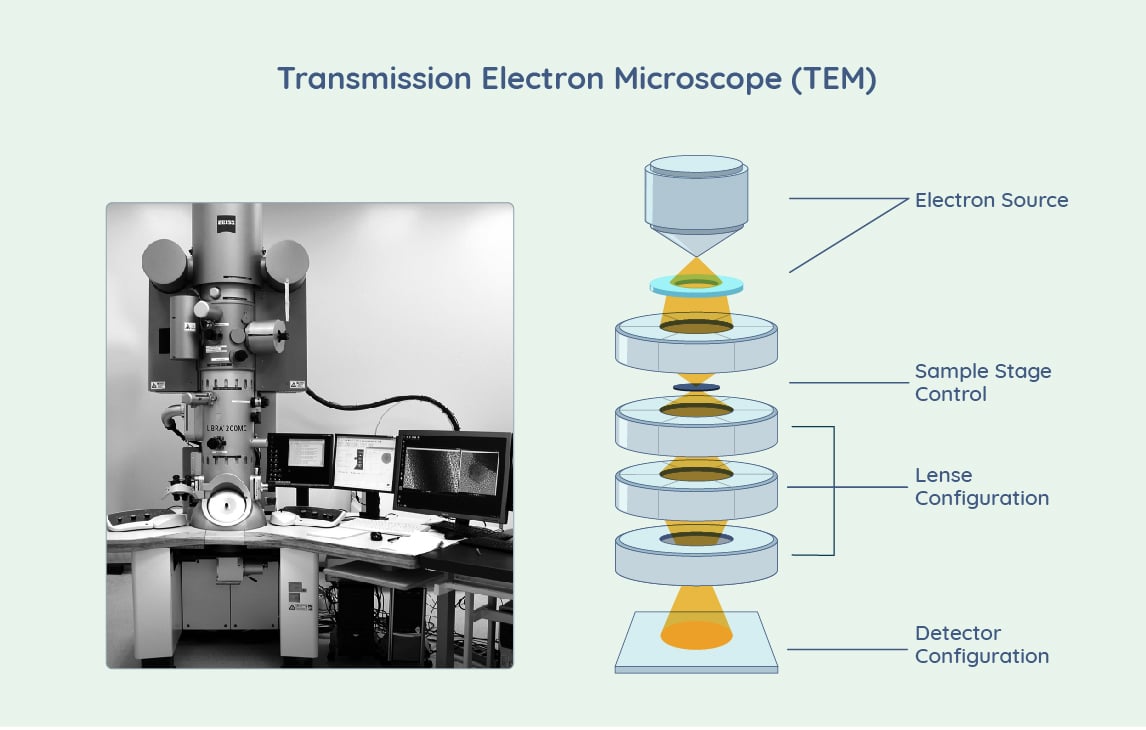
- Power and Resolution – Two types of electron guns are available for focusing electron beams on the samples to be imaged. Thermionic, which use tungsten and lanthanum hexaboride sources, and field emission sources, either cold field emitter or Schottky. The accelerating voltages can range from 120-300 KeV — much higher than those required for SEM instruments. The use of electron sources with elevated voltage requirements has an impact on price.
- Imaging Analysis – TEM instruments can analyze multiple types of imaging samples, including hydrated (cryo) and dehydrated samples. In addition to high-resolution TEM, imaging techniques can include electron diffraction, tomography, single-particle analysis, in situ imaging, and others. Analytical capabilities can include energy dispersive x-ray microanalysis (EDX), electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS), and other techniques. Automated sample loading, as well as automated data acquisition software, can add to the efficiency of TEM systems. All of these capabilities come at a cost, and may or may not be required for certain applications.
- Sample Preparation and Cryo-EM – Specialized sample preparation techniques and hardware are needed for creation of electron transparent, thin samples for imaging. Sample preparation processes are often tedious and require specialized tools and reagents. Modern TEM technologies, such as those using variable pressure (VP) with specialized electron detectors, creates imaging conditions that enable biological samples to be viewed with minimal preparation. Environmental TEM allows samples to be imaged under low vacuum in native hydrated state. For cryo applications, an attachment is typically required consisting of: a cryo chamber for freezing, a metal coating device to apply a conductive metal coating, and a cold stage to keep the sample stable during the imaging process. Microtomes or cryotomes are required for preparation of ultra-thin sections and cryo-sections. All of these sample preparation tools and considerations impact the price of the setup.
Dual Beam Electron Microscope (SEM/FIB) Price Factors
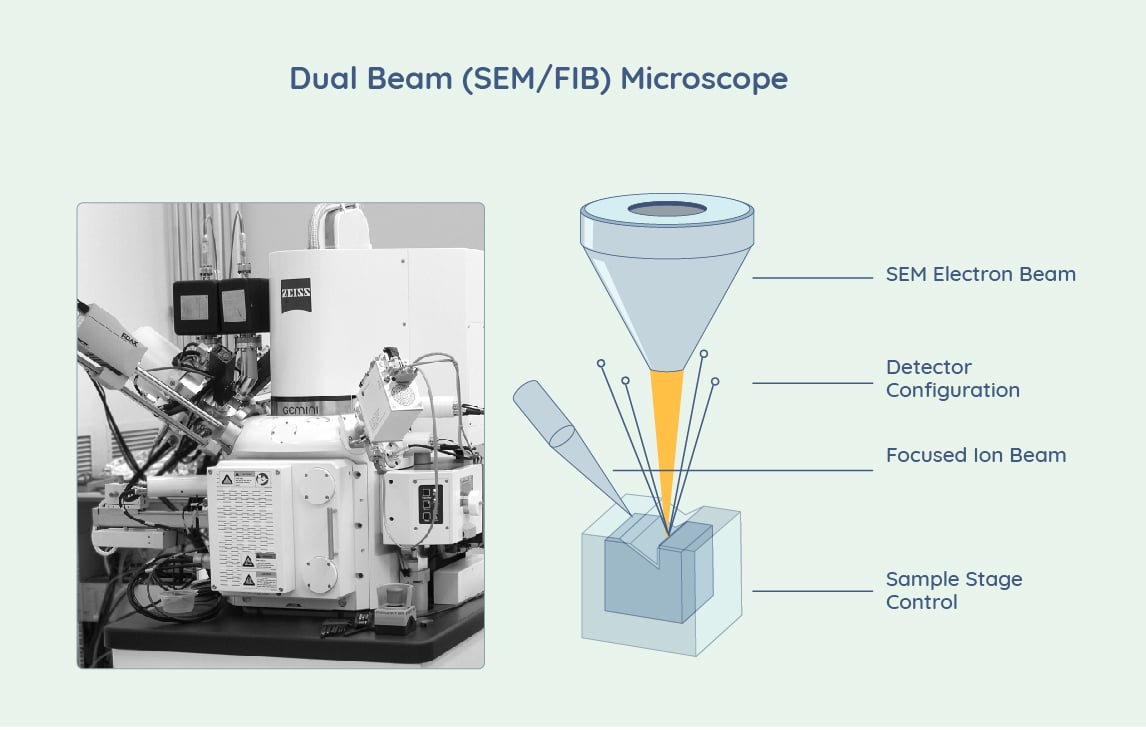
- Dual beams are primarily used for specific processes including cross-sectioning, polishing, and patterning areas for focused image analysis.
- Although the SEM is typically identical to that used in a stand-alone SEM instrument, the ion beam sources can vary, differing in the element used to create the focused ion beam.
- The price considerations of an SEM instrument must be combined with FIB price factors such as beam source, gas injection system, high-throughput functionality, and other details, in order to arrive at an accurate cost for a dual beam setup.
What Determines the Cost of an Electron Microscope?
As detailed above, main cost determinants of electron microscopes include the following:
- Type of EM instrument for the desired application
- Resolving and magnification power
- Current and voltage of the electron beams
- Quality and performance of the electron emitters
- Quality and type of the electron detectors
- Vacuum source required for the specimen chamber
- The types of specimens to be imaged and any specialized components
- Image analysis software and viewing setup
In addition to the actual physical instrument costs, there are a host of additional factors to consider when determining cost of an EM setup.
- Facilities and fabrication – EM setups typically require acoustic and vibrational isolation chambers, magnetic field canceling systems, and other environmental control features. Therefore, a facility is needed to house the EM, often in magnetically and vibrationally shielded locations.
- Operating Costs and Consumables – The power consumption of the instrument should be considered, as should the recurring costs of consumables. Setups consume 50 eV for SEM to between 100 keV and 400 keV for TEM, whereas high-resolution instruments come with kilovolt power specifications.
- Training, Service, Maintenance, and Repair – Training the right personnel to run and maintain the instrument is a serious consideration. Budgeting to account for service and repair are other important factors to build into the cost of operations.
Summary
There are many details to be aware of when researching electron microscope setups. These range from physical features of the instruments themselves, to the facility, operating needs, and other important factors. All of these have a direct impact on cost of ownership. In deciding to buy new versus used, also weigh the needs of the current work versus the potential usefulness of new technology on future work.
Electron microscopes are highly sophisticated and powerful imaging devices that can be a very expensive investment of time and money. It’s important to carefully and thoroughly evaluate your needs, expectations, and cost considerations before purchasing.










